| Seite 3 |
Making Plans
Future Tense and wollen
- The future tense is formed much like a sentence with a modal verb.
- The auxiliary verb is werden.
- The infinitive is placed at the end of the sentence.
- werden and the modal verb wollen are often confused, because werden is the German equivalent of "will" in English, as in "We will go to the Park on Saturday." But "Ich will am Samstag in den Park gehen" means "I want (not: I will) to go to the Park on Saturday".
- The verb werden also has an irregular conjugation pattern (see below).
werden ich werde wir werden du wirst ihr werdet es wird
sie wird
er wirdsie werden Sie werden 

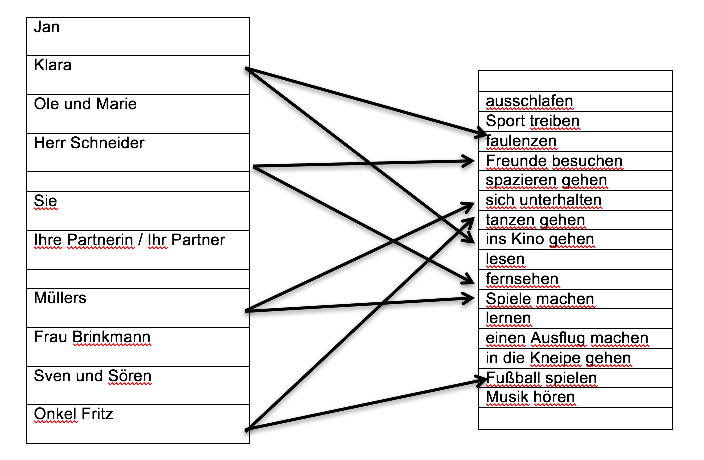
Übung 4-3a: Pläne machen. Teil A (Teil B steht auf Seite 11) Sie haben die Hälfte der Informationen. Fragen Sie ihre Partnerin / ihren Partner nach der anderen Hälfte. (You have half the information. Ask your Partner for the other half.)
Before you begin, draw arrows from the box "Sie" to two activities to indicate your plans for the weekend.Wortschatz:
- ausschlafen: catch up on sleep
- vorhaben: to plan (separable prefix: Was hat Klara am Wochenende vor? = "What is Klara planning for the weekend?"
- faulenzen: goof off, be lazy
- sich unterhalten: to have a good time
- der Ausflug -¨e: trip, outing
Redemittel:
A: Was hat Klara am Wochenende vor?
B: Sie wird am Wochenende ins Restaurant gehen.
A: Was haben Müllers am Wochenende vor?
B: Sie werden sich am Wochenende unterhalten und Spiele machen.
A: Was hast du am Wochenende vor?
B: Ich werde am Wochenende faulenzen und in die Kneipe gehen.
Familienpolitik

The German federal government includes a cabinet-level office (called a ministry) for family policy. Nothing vaguely related to family policy, or even the concept of family policy, exists in the Cabinet of the United States.
Family is considered very important in Germany, although traditional gender roles continue to change. About 65 percent of mothers participate in the labor force (Women comprised 47 percent of the total U.S. labor force), and the number of dual income couples without children has increased. This is evident in that over 40% of German women between ages 25-49 reside in childless households, which is well above the European average. Germany and the United Kingdom also share the record for highest average age at which women choose to have their first child.
Germany is considered a welfare state with an all-embracing system of health, pension, accident, long-term care, free education at all levels, and unemployment insurance. Approximately 27% of the GDP* is channeled into public welfare spending. In the United States, welfare costs are estimated at 2.51% of GDP in 2015. Income taxes in both countries, ranging from 14% to 45% in Germany, compared with 10% to 39.6% for the USA, depending on income levels, support the welfare state programs.
In 2001, the German government introduced "Parent Time" (Elternzeit), which obligates all employers to preserve the same or comparable position to which mothers (or fathers) may return for as long as three years. In the USA, Family and Medical Leave Act of 1993 (FMLA) mandated a minimum of 12 weeks unpaid leave to mothers for the purpose of attending to a newborn or newly adopted child (the lowest level of maternity leave in the industrialized world); there is no paternity leave. The loss of wages during this time compel many pregnant women work right up to the time of birth.
In 2007, the German government introduced the program called parents' money (Elterngeld). After the birth of a child, if either parent decides to leave work for a certain period of time, the state pays 67% of the monthly average net income, not to exceed 1,800 Euros ($2,200) per month. Parents who were not working before they became parents receive the minimum amount of 300 Euros ($355) monthly added to the family income. Parent's money is granted for a maximum period of 14 months starting with the day of the birth. The period of 14 months can be divided between both parents, though one parent can only ask only for a maximum of 12 months. A single parent is eligible for the full 14 months.
Child Allowance (Kindergeld) is granted independently from income. It is closely related to the number of children at home and is determined as follows: for the first and the second child, 184 Euros ($218) per child per month is allocated to the family to help support the child(ren); for the third child, 190 Euros ($225) per month is allocated, and for the fourth or more children, 215 Euros ($254) is provided to the family. It is granted until the age of 18, or until the age of 25 years, if the child is still following apprenticeships or attending higher education institutions.
In the USA, financial relief for child care is provided only indirectly through a tax deduction of $1,000 per child per year (a deduction that could soon be cut). This amounts to child support of $83 per month, but only for those who pay taxes, and only until a child is 17 years old. In the United States, 20% to 35% of child care costs for pre-school day care (depending on income level) can also be deducted from taxes. Child care support in the USA is regarded as a matter for the individual states to manage, as well, so comparisons between Germany and the USA at the national level are complicated.
In the first year after a child is born, most German parents, especially mothers, stay at home. Parent's money gives them a certain amount of flexibility. Starting in 2013, every child over the age of one is eligible, legally, to ask for a spot in a child care facility.
Despite the support Germany provides families with children, the birth rate in Germany is much lower than in the USA, 1.5 vs 1.84 children per woman, which is why Germans are concerned about the aging population and the decrease in tax-paying citizens.
* Gross domestic product (GDP) is the best way to measure a country's economy. GDP is the total value of everything produced by all the people and companies in the country.
- Kapitel 4: Seite 1
- Kapitel 4: Seite 2
- Kapitel 4: Seite 3
- Kapitel 4: Seite 4
- Kapitel 4: Seite 5
- Kapitel 4: Seite 6
- Kapitel 4: Seite 7
- Kapitel 4: Seite 8
- Kapitel 4: Seite 9
- Kapitel 4: Seite 10
- Kapitel 4: Seite 11