Quiz 2 - Sections 1.1-1.3
You may use your calculators to check yourself and to perform algebra, but show your work for credit.
For each of the following find the limit using analytical techniques when possible. If the limit does not exist, state what type of behavior the function has at that point and support your answer with graphical evidence or a table of values.
(1)
(2)
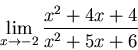
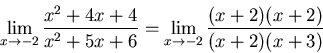
(3)
A graph shows that
![]() oscillates infinitely often
in the range of -1 to 1 as x approaches 0.
oscillates infinitely often
in the range of -1 to 1 as x approaches 0.
(4)
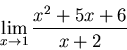
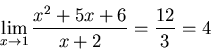
direct substitution works